Chapter 14: External Diffusion Effects on Heteregeneous Reactions
Example: Relative Rates of Diffusional Transport
What are the relative rates of transport of a through a stagnant gas and equal molar counter diffusion for the same concentration boundary conditions. Recall the relative concentration profiles were
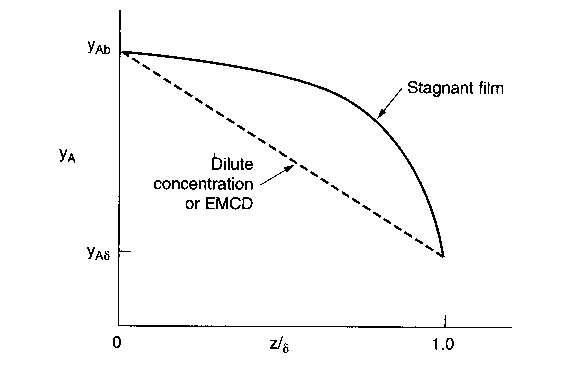
EMCD
\( W_{Az} = \frac{c D_{AB}}{\delta} \left( y_{Ab} - y_{As} \right) \)
Stagnant film
\( W_{Az} = \frac{c D_{AB}}{\delta} \ln\left( \frac{1 - y_{As}}{1 - y_{Ab}} \right) \)
Ratio of transport rates
\( R = \frac{W_{Azs}}{W_{AzEMCD}} = \frac{\ln\left( \frac{1 - y_{As}}{1 - y_{Ab}} \right)}{y_{Ab} - y_{As}} \)
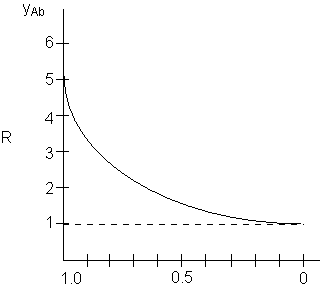
Let yAs = 0 @ surface (e.g., infinite reaction)
\( R = \frac{\ln\left( \frac{1}{1 - y_{Ab}} \right)}{y_{Ab}} \)
We now will compare the relative rates as a function of the mole fraction, yAb, of the diffusing species, A, at the upper boundary z = 0.
|
y Ao 0.999 0.99 0.90 0.8 0.7 0.6 0.5 0.4 0.3 0.2 0.1 |
R 6.91 4.65 2.56 2.01 1.72 1.53 1.39 1.28 1.19 1.12 1.65 |
yAo |