Friction: "the force that resists relative motion between two bodies in contact"
Merriam Webster:"the force that resists relative motion between two bodies in contact"
- "Friction force" is tangential to the contacting surfaces of the two bodies.
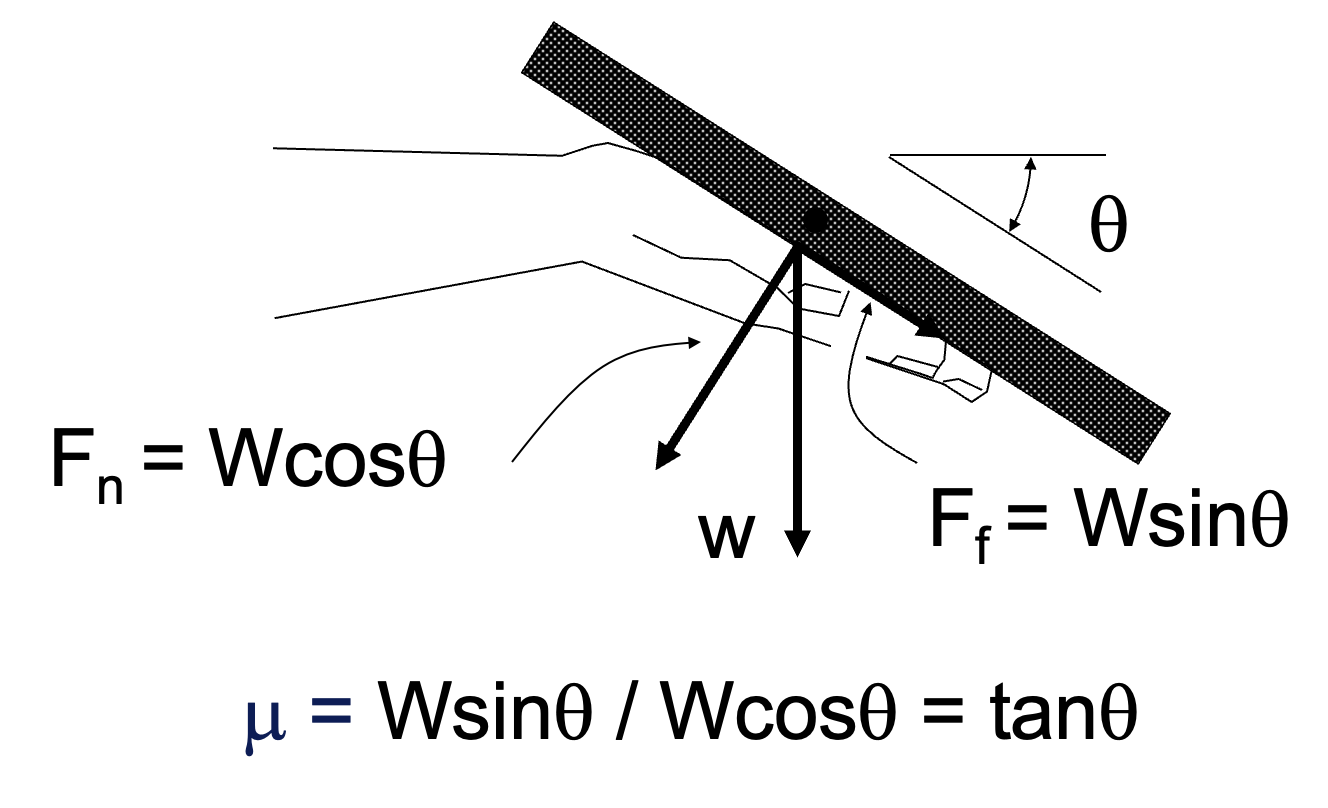
- "Contact force" act perpendicular or "normal" to the surfaces of the contacting bodies. (see Fig 1)
- The "Coefficient of Friction," CoE, is defined as the ratio of the Friction force to the Contact force:
CoF = Friction force / Contact force

CoF=
Published hand friction Data
| Material (n=42) | Dry | Moist (n=42) | Combined (n=84) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sand Paper (#320) | -- | -- | 0.61±0.10 |
| Smooth Vinyl | -- | -- | 0.53±0.18 |
| Textured Vinyl | -- | -- | 0.50 + 0.11 |
| Adhesive Tape | 0.41±0.10 | 0.66±0.14 | -- |
| Suede | 0.39±0.06 | 0.66±0.11 | -- |
| Aluminum | -- | -- | 0.38±0.13 |
| Paper | 0.27±0.0 | 0.42±0.07 | -- |
Buchholz B, Frederick L Armstrong T. An investigation of human palmar skin friction and the effects of materials, pinch force and moisture. Ergonomics 31(3):317-325, 1988.
Bobjer O, Johansson SE, Piguet S. Friction between hand and handle. Effects of oil and lard on textured and non-textured surfaces; perception of discomfort. Applied Ergonomics. 1993 Jun 1;24(3):190-202.
A simple method for measuring static coefficient of friction, CoF
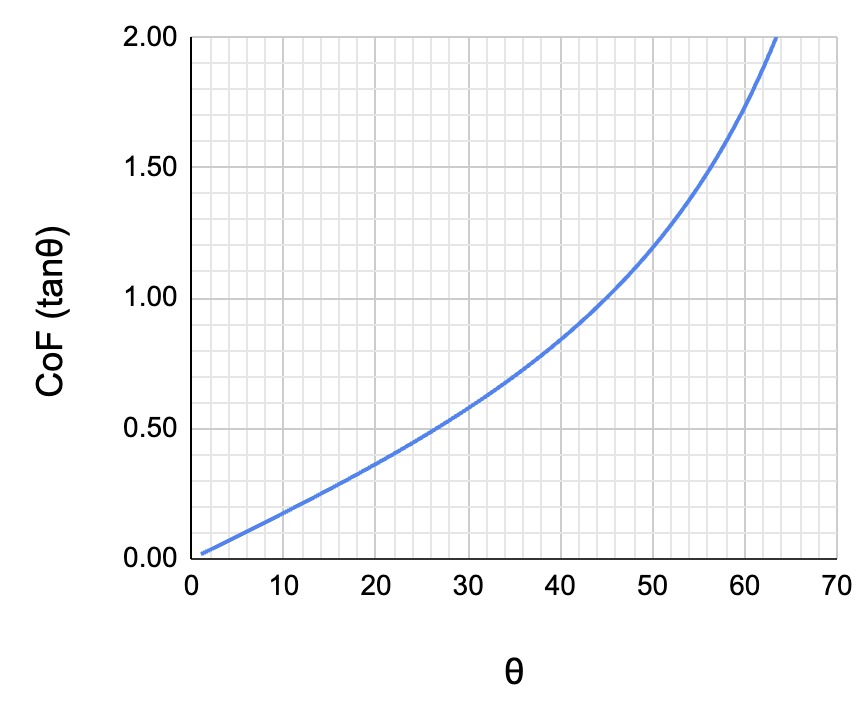
The static CoF can be estimated by placing an object on a flat hand and calculating the tagent of the tilt angle at which the object begins to slide (see Fig 2) (Seo et al. 1999).
The CoF will be affected by the moistness of the skin, contaminants, and contrary to what we were taught in basic physics the weight of the object. The moistness of the skin may change with environmental condition and the materials being touched. Materials that absorb water cause the skin to dry and reduce fiction.
 |
 |
| Enter an angle in degrees: | |
Seo N, Armstrong T, Drinkaus P. A Comparison of Two Methods of Measuring Static Coefficient of Friction at Low Normal Forces: A Pilot Study. Ergonomics 52(1):121-135, 2009.