
|
|
 |
  |
|
|

|
Jessica Schwartz, Ph.D.
Professor of Physiology
Director, Program in Cellular and Molecular Biology
Ph.D., Harvard 1974
6815 Med. Sci. II
(734) 647-2124
jeschwar@umich.edu
|
To understand the molecular basis of growth regulation, this laboratory studies mechanisms for regulation of gene expression by growth factors. A
major goal is to identify signal transduction pathways between growth factor receptors and target genes in the nucleus.
One of our key approaches is to focus on the actions of growth hormone, a critical regulator of normal growth, and related factors which also signal by
receptors in the cytokine receptor superfamily, including interferons and interleukins.
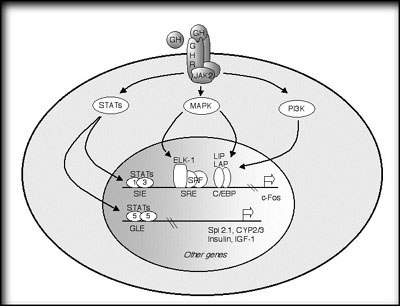
Click above to open larger diagram in new window.
By examining how growth hormone activates the proto-oncogene
c-fos, we have identified three different signaling pathways that culminate on different transcription factors associated with the c-fos promoter:
- The
Jak-STAT pathway mediates activation of STAT transcription factors by tyrosine phosphorylation,
- The Ras-MAP kinase pathway culminates in an
activating serine phosphorylation of the transcription factor Elk-1,
- A potentially inhibitory pathway regulates the transcription factors C/EBP beta
and delta, which have been implicated in cell differentiation and proliferation.
Current work examines cross-talk among the multiple signaling pathways
and potential interactions among the transcription factors regulated by growth hormone. To assess molecular mechanisms by which growth factors
promote differentiation of target cells (e.g. adipocytes), we are also examining effects of growth factors and cytokines on the function of genes
associated with cell differentiation and cell cycle regulation. Ultimately, our studies will provide insight into how regulation of early gene expression
contributes to changes in cell growth, differentiation and metabolism, and will be important for an understanding of diseases such as cancer and
diabetes.
|
|
|